
Blog Articles
Obfuscate JS to Strengthen React Security
Table of Contents
In the realm of web development, ensuring the security of applications built on React.js is paramount. As the popularity of React continues to soar, so does the need to safeguard sensitive codebases from potential threats and vulnerabilities. One powerful tool that developers can utilize to enhance React security is obfuscate JS. By obfuscating JavaScript code, developers can obscure its logic and structure, making it challenging for unauthorized users to understand and manipulate. In this blog, we delve into the concept of using obfuscate JS to strengthen React security. We explore how this technique works, its benefits in protecting against unauthorized access and intellectual property theft, and practical considerations for implementing obfuscation techniques in React projects. Join us as we uncover the importance of obfuscate JS in fortifying the security posture of React applications.
We are starting with the problem statement as well as setting up the solution:
Initial Requirements
– Latest NodeJS and NPM
Latest start with setting up application:
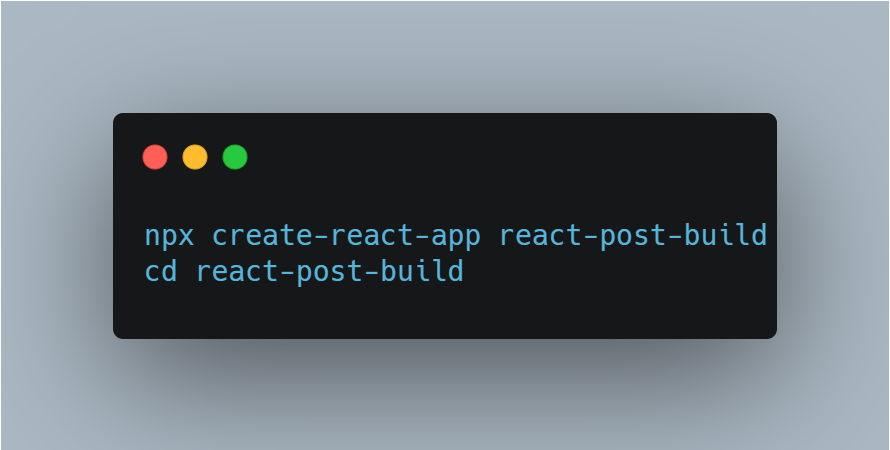
Create React Application:
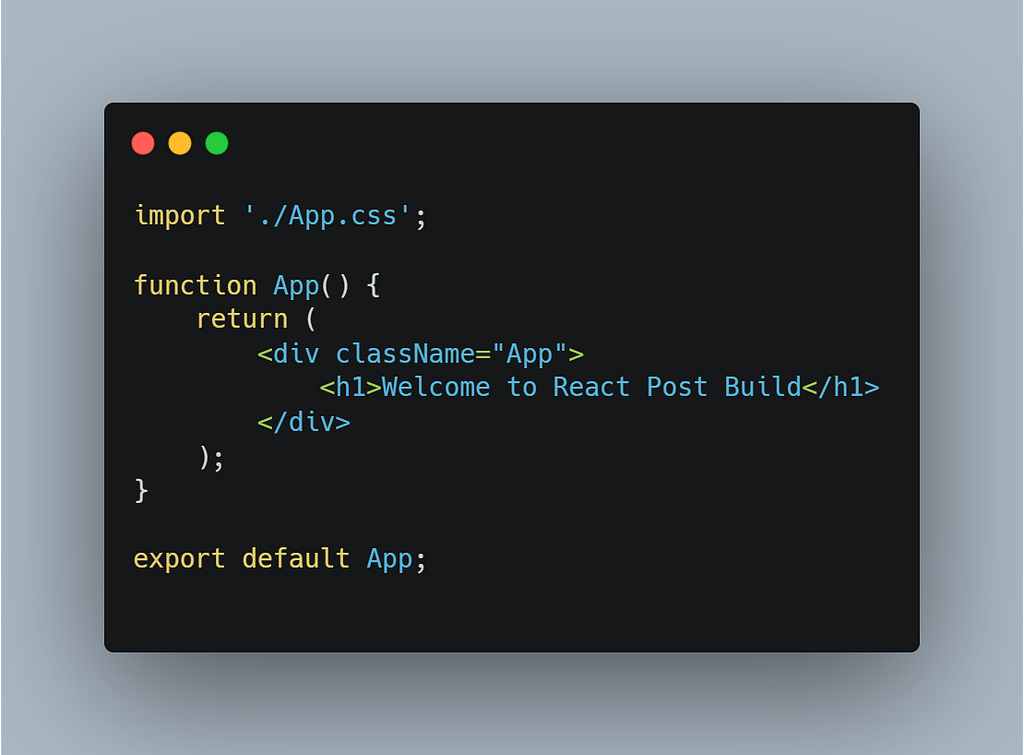
Update the ‘App.js’ with simple addition of h1 tag:
Start React Project:

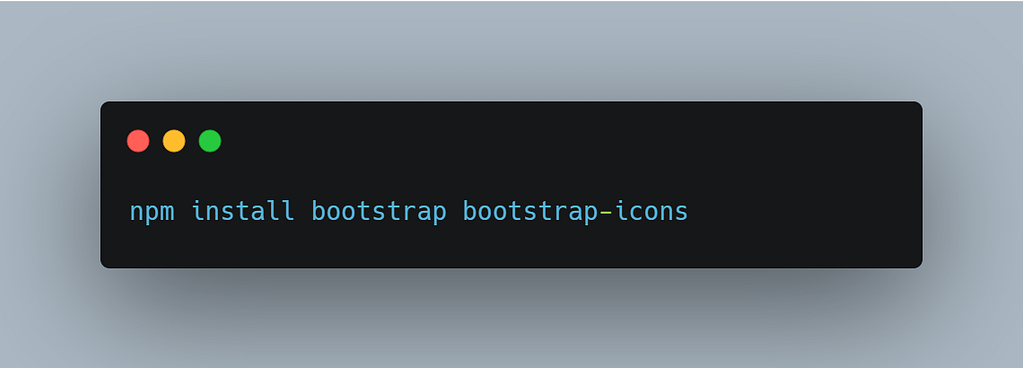
Install Bootstrap framework:
Execute the following npm command to install the Bootstrap and icons.
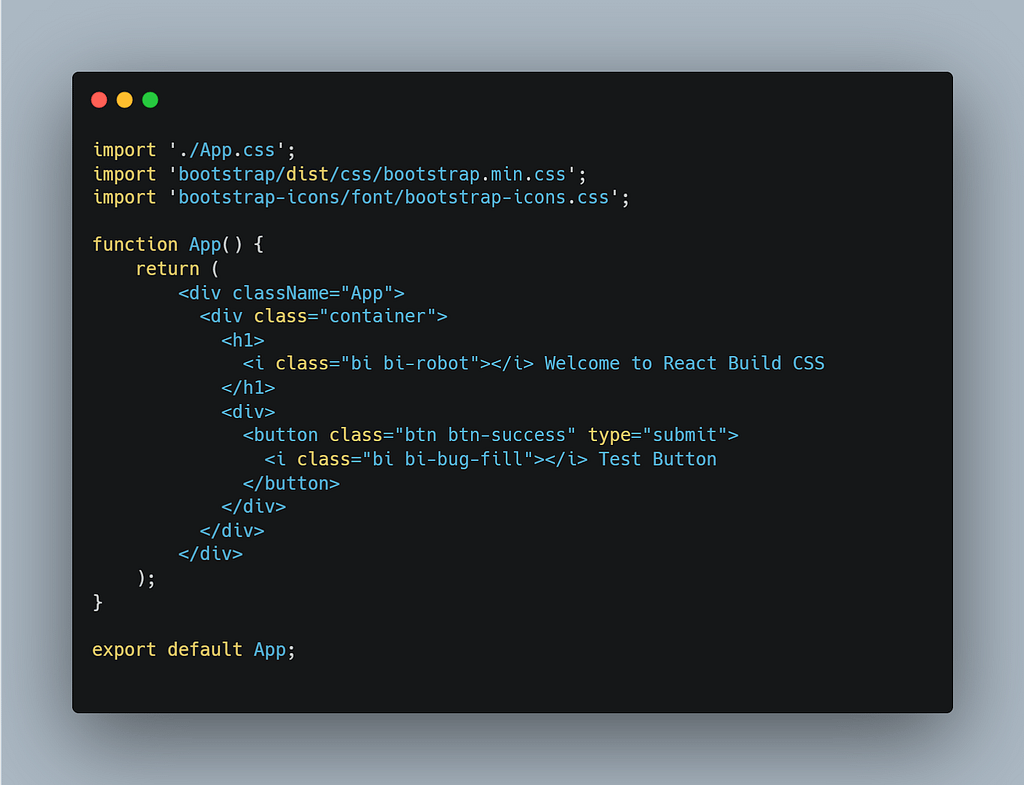
Configure Bootstrap with Application:
Import Bootstrap CSS and apply classes to HTML.
Remove Unused CSS:
We are going to implement this with the production build process.
PurgeCSS:

purgecss.js
Create an external script file, here the following script analyzes the build folder and minimizes the CSS file. Create a scripts folder under the project src directory.
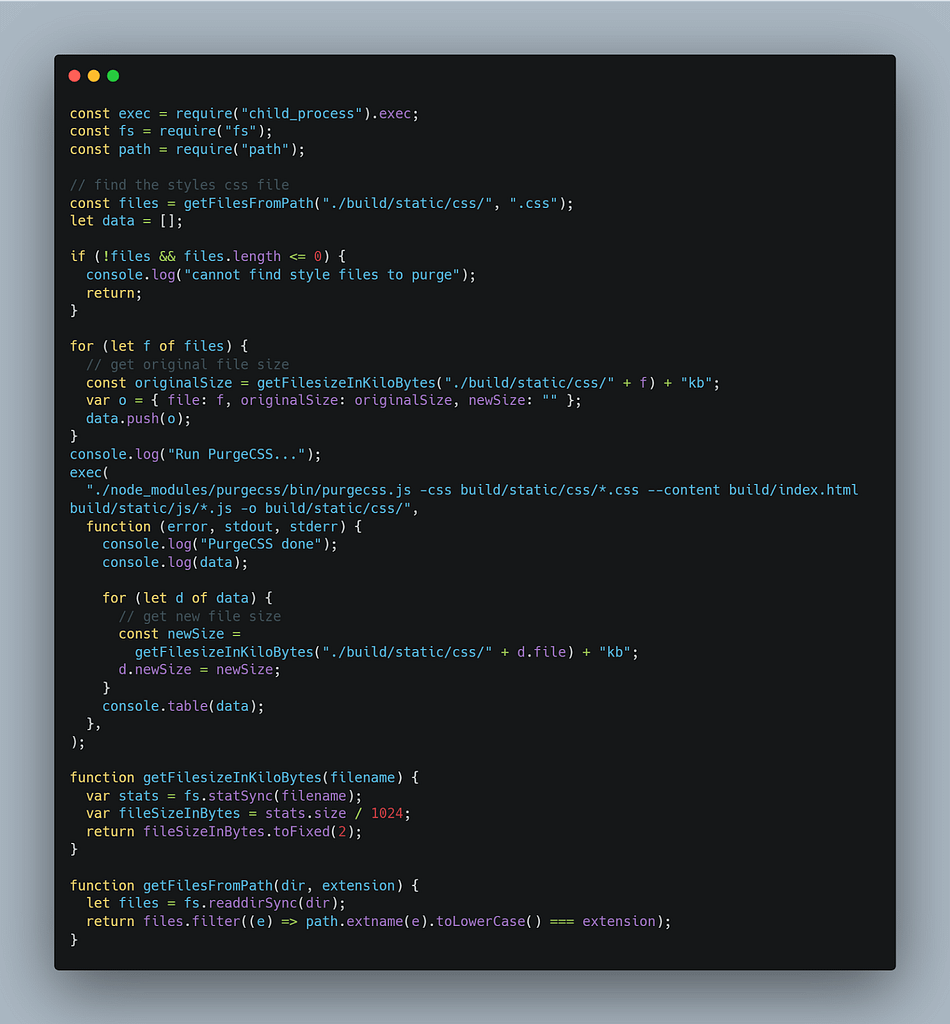
package.json:
Update the package scripts and include ‘purgecss’ command with the build command.

Build Project:
Now the following command will execute the project build with purge CSS commands.
| npm run build
After the application build, this will remove the unused CSS and creates a new small CSS file.
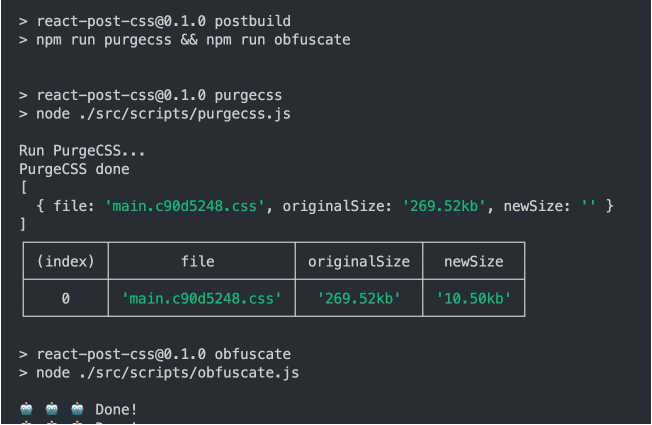
Obfuscate JavaScript:
Obfuscate JS tool converts code to a cryptic format, enhancing security by making it difficult to copy and steal. Protect your source code with obfuscate JS, deterring unauthorized access and protecting intellectual property.
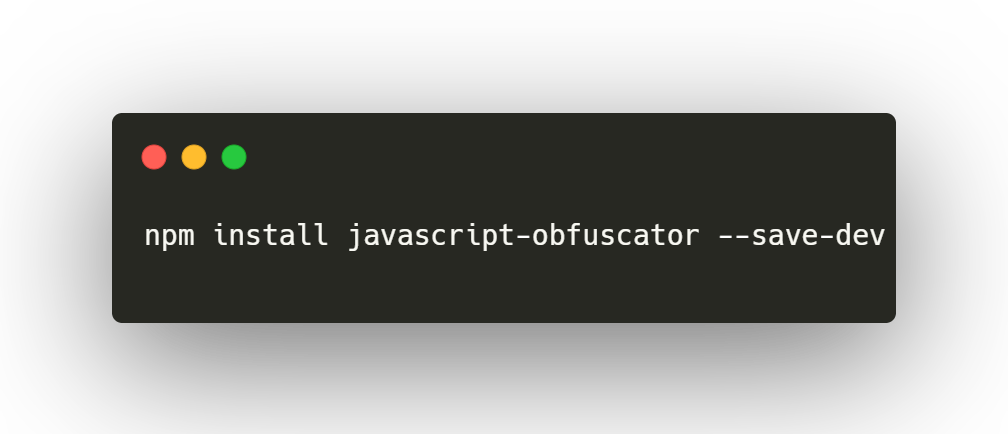
Install Javascript Obfuscator:
Include javascript-obfuscator plugin in dev dependencies to obfuscate js.
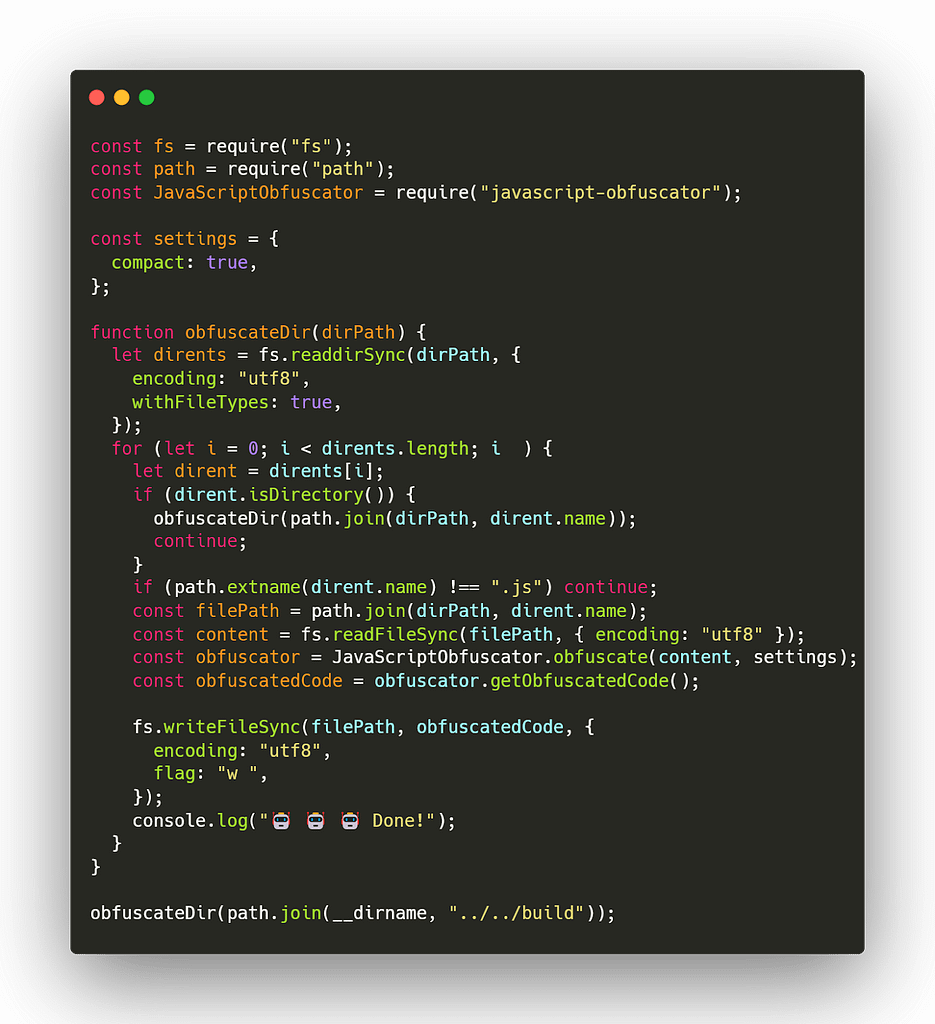
obfuscate.js:
External executable files and analyze the build files and convert all of the JavaScript files. Copy this file under the application src/scripts folder.
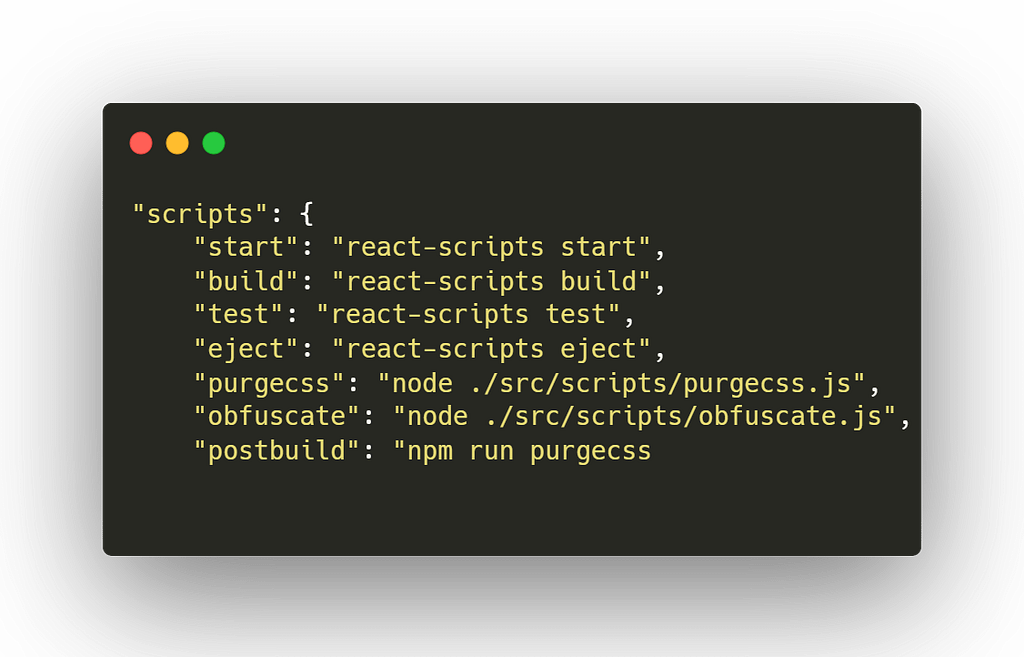
Final package.json:
Combine all the external scripts and include the post-build command.
Note: If you are using a translated language file, don’t include any CSS styles. Purge CSS analyzes only JS and HTML files.
Conclusion
In conclusion, leveraging obfuscate JS in React projects offers a robust strategy to bolster security measures. By transforming JavaScript into a cryptic format, obfuscation deters unauthorized access and safeguards intellectual property. This practice enhances the resilience of React applications against potential threats, making it challenging for adversaries to reverse engineer or exploit vulnerabilities. As a result, integrating obfuscate JS into the development workflow stands as a dynamic measure to reinforce React security, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of codebases in an forever changing digital landscape.
For additional insightful articles and information on custom software development services, please reach out to us.

Get a Fast Estimate on Your Software Development Project
We are committed to delivering high-quality IT solutions tailored to meet the unique needs of our clients. As part of our commitment to transparency and excellence, we provide detailed project estimations to help our clients understand the scope, timeline, and budget associated with their IT initiatives.



